How to Choose the Right PoE Power Sourcing Equipment (PSE)
Step 1: Understand Device Requirements
Before choosing PoE power supply equipment, it's essential to have a deep understanding of the powered devices. Examine the power specifications of each device carefully and confirm its support for PoE standards such as 802.3af, 802.3at, or 802.3bt, as well as passive PoE. Ensure that the selected PoE power supply equipment complies with these standards to avoid compatibility issues.
Step 2: Consider Layout and Calculate Total Power Requirements
After understanding the power and standards of each device, determine the network layout, specify the number of devices that need simultaneous connections, and calculate the total power requirements. This helps ensure that the chosen PoE power supply equipment has sufficient power to support all connected devices.
Step 3: Choose Suitable PoE Equipment and Power Based on Budget
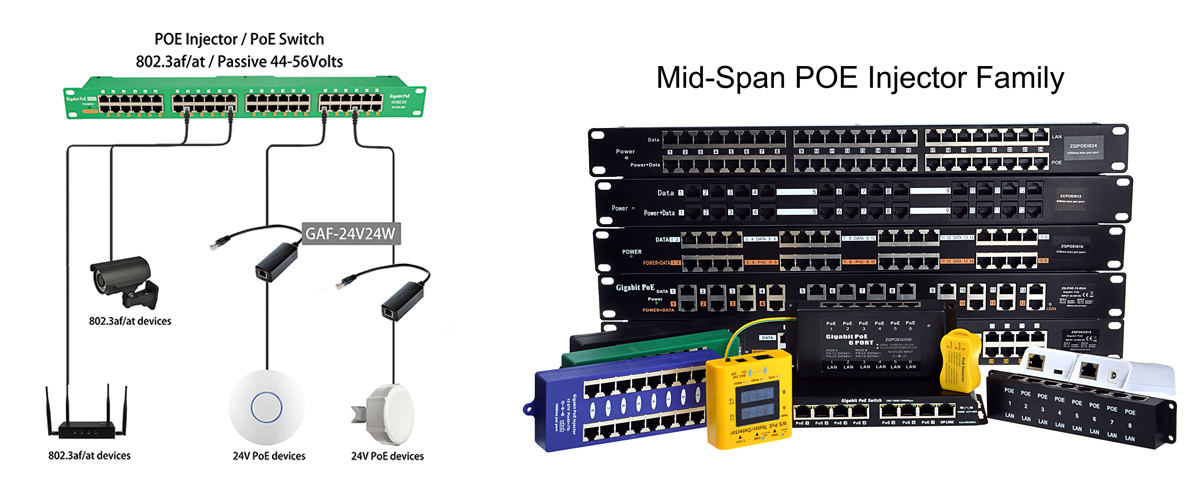
Once power consumption and requirements are confirmed, choose suitable PoE power supply equipment and power sources. If the budget is limited, consider opting for 48V passive PoE instead of standard 802.3af/at PoE. Additionally, if the existing switch doesn't support PoE, and most powered devices require PoE, or replacing the PoE switch and the entire network architecture is cost-prohibitive, consider selecting midspan PoE as a supplementary option.

When selecting PoE power supply equipment, you may encounter the following considerations:
1) Choosing between Standard PoE and Non-Standard PoE
Standard PoE (such as 802.3af/at/bt): Adheres to IEEE standards with intelligent handshaking and level allocation; Provides higher security and reliability; Suitable for scenarios with high requirements for these factors.
Non-Standard PoE (Passive PoE): Adopts a forced power supply method, lacking intelligent pairing; Lower cost, suitable for simple scenarios and cost-sensitive customers.The choice between standard PoE and non-standard PoE often depends on the specific application's requirements.
2) Differences between PoE Switches and PoE Midspan
PoE Switch: One-to-many power supply, suitable for scenarios with multiple device connections.
PoE Midspan: One-to-one power supply, can be used with non-PoE switches, providing flexible options.
Adding PoE midspan devices can complement insufficient power supply, upgrade existing networks, or provide a more flexible power supply method.
3) Differences between 48V/56V Passive PoE and Standard PoE
Standard PoE (802.3af/at): Uses handshaking protocols for intelligent pairing, providing a working voltage of 37-57V.
Passive PoE: Forced power supply, usually providing 48V, suitable for devices supporting the 802.3af/at standard. There is also 24V Passive PoE.
48V Passive PoE is typically compatible with standard PoE devices, but attention to device specifications is needed to ensure compatibility.
4) Powering Modes A and B
Mode A: Supplies power through 1/2 and 3/6 pairs, supporting 1/2+ 3/6- or 1/2- 3/6+.
Most devices support both Mode A and Mode B power supply, especially in the 802.3bt standard, using 4 pairs of wires for power and data transmission.
Mode B: Powers through 4/5+ 7/8- or 4/5- 7/8+, suitable for brands like Mikrotik and UBNT.
5) Does PoE Power Supply Equipment Include Power Supplies?
Some PoE power supply devices have built-in power supplies, but our company's PoE power supply equipment uses external power supplies.
Users can choose a suitable power supply based on the device's requirements. Passive PoE midspan supports voltage input ranging from 12-56V, while active PoE midspan supports 44-56V voltage.
When choosing a power supply, consider the device's power consumption and the required voltage.
Example of PoE Power Supply Equipment Selection Scenario:
Scenario:
The customer's existing switch does not support PoE, and they plan to connect 8 cameras supporting 802.3af PoE/12V DC, with a maximum power consumption of 9W per camera. Additionally, they have 2 24V passive PoE Gigabit-speed wireless access points (AP), with each AP having a maximum power consumption of 12W. Furthermore, the customer has 2 cameras that do not support PoE, with a power consumption of 5V 1.4A (7W). The customer wants to connect all devices in one network architecture.
Analysis:
Considering the devices, most of them support the 802.3af PoE standard. If the budget allows, it is advisable to consider upgrading the power supply equipment to a standard PoE switch or choose a midspan device that complies with standard PoE to supplement and upgrade the entire network architecture. For budget-constrained customers, choosing a 48V passive PoE midspan device is an alternative.
For the wireless AP using 24V passive PoE and non-PoE cameras, converters and splitters can be considered for compatibility.
Calculating Total Power Requirements:
Total power requirement for 8 cameras supporting 802.3af PoE: 72W.
Total power requirement for two 24V passive PoE devices: 24W.
Additional power consumption for 2 non-PoE cameras: 14W.
Total connected devices: 12, with a total power requirement of 110W.
Based on this information, whether choosing a PoE switch or a PoE midspan device, the power capacity should not be less than 110W to ensure sufficient port connections.
Conclusion:
Flexibly choose PoE power supply equipment and power sources based on actual needs and budget. Note that if the devices support 802.3af PoE/12V DC, a 48V power source is required when using PoE functionality. When using a 12V power source, direct DC power can be used. Such careful considerations ensure the stability and reliability of the network.
